Treatment of Uncertainties with Algorithms of the Paraconsistent Annotated Logic ()
1. Introduction
The data processing systems frequently face situations that represent scenes of uncertainties, ambiguities and inconsistencies. These situations appear because the database which is to be worked is generally incomplete or inexact [1-2]. For an efficient process data handling the information treatment system must be ready to deal with these adverse situations. Data processing systems which deal with uncertainty knowledge must be able to represent, manipulate and communicate data which is considered imperfect [2-3]. Most of the times, the data which we conventionally call imperfect are within those representing inaccurate, inconsistent, partially ignored and incomplete information.
The Uncertainties in Database
The presence of uncertainty in a system based on knowledge processing can be occasioned by a variety of information sources [2-3]. Among these we should mention; the ones we know to be of partial reliability; the ones presenting inaccuracy stemming from the representative language in which the information is shown; the ones not showing completeness of information and those which summarize or aggregate information from multiple sources [4-5]. In the area of treatment of signals extracted from nonexact knowledge there are many formal models available for the treatment of uncertainties, but in many cases these proceedings have been achieved through approaches based in combinations and representations of rules which are not structured by a well-based theory, as well as well-defined semantics [2,3,5].
An intelligent system for decision making must be robust and well-based to meet theoretical criteria, therefore, it needs to be subsided by an adequate treatment of uncertainties theory which will offer possibilities, within certain limits, at any verification, independently from its application [6,7]. Considering these problems regarding uncertainties the methods for uncertainty treatment in this paper presented use the basic concepts and theoretical foundations of Paraconsistent logics (PL), obtaining a quantitative evaluation through its representative Lattice [8]. All manners of application and results are obtained through Paraconsistent Annotated Logic with annotation of two values (PAL2v) fundaments [9].
The organization of the paper is as follows: in the section 2 the basic concepts, the interpretation and the main equations of the LPA2v Logic are presented. In section 3 the main algorithms of the LPA2v used in the Paraconsistent System of Treatment of Uncertainties are presented. In the section 4 a numeric application example is shown, and, in the section 5 are presented conclusions about the development of the PAL2v application research.
2. The Paraconsistent Logics
Within the many ideas in the non-classic logics a family of logics has arise that showed as its main theoretical foundation the revocation of the non-contradiction principle. These non-classic logics that consider the concepts of contradiction in its structure had been called Paraconsistent logics (PL) [10]. Paraconsistent Logic is, therefore, a non-classic logic, which repeals the principle of noncontradiction and takes the treatment of contradictory signals in its theoretical structure. A summary of the theoretical principles that sustain paraconsistent logics [3,4,9] may be seen as thus: It is known that the statements demonstrated as true in a theory are called theorems and if all the sentences formulated in their language are theorems, it is said to be trivial. It is also known that a theory is consistent if among its theorems there aren’t those that affirm something which is the negation of other theorems in the same theory. In case it happened, the theory would be called inconsistent [3,9]. Given a theory (deductive) T, settled on logic L, it is said to be consistent if there aren’t such, that one is the negation of the other; in a contrary hypothesis, T denominated inconsistent. The theory T is called trivial if all the sentences (closed formula) in its language are theorems; if this does not happen, T is non-trivial. If L is one of the common logics like the classical, the theory T is trivial if and only if it is inconsistent. In other words, logics like these do not separate the concepts of inconsistency and triviality, because according to classical logic, an inconsistent theory is also trivial, and reciprocally, because if a contradiction is accepted as valid, then any conclusion would be possible. As this is an undesired result, classical logic does not admit the contradiction as an acceptable element without making it trivial. Logic L is called paraconsistent if it can work as the basis of inconsistent and nontrivial theories [8,10]. This means that, except in certain specific circumstances that go beyond our study, paraconsistent logic is able to manipulate inconsistent information systems without the risk of trivializetion [9].
The pioneers of paraconsistent logics were the Polish logician J. Lukasiewicz [11] and the Russian philosopher N. A. Vasilév, who simultaneously, around 1910, in an independent manner, suggested the possibility of a logic which would restrict the principle of contradiction. The initial systems of Paraconsistent logics, containing all the logical levels, with propositionals, predicates and descriptions, as well as higher-order logic, are credited to N. C. A. Da Costa (1954 onwards) [9,10]. It happened in an independent manner, and there are, currently, paraconsistent systems of group theory, strictly stronger than the classic ones considered as paraconsistent subsystems [4,10].
2.1. Lattice Associated with the Paraconsistent Annotated Logic
The Paraconsistent Annotated Logic (PAL) may be represented in a particular way through a Hasse diagram in which, intuitively, the constants in the vertices of a lattice will show extreme logical states to the propositions [4,6, 8,9].
The Paraconsistent Annotated Logic with Annotation of Two Values—PAL2v
As seen in [7] and [9] it is possible to obtain a representation on how accurate the annotations (or the evidences) are on a proposition P using a lattice formed by ordained pairs, such as: t = {(m, λ)|m, λÎ [0, 1] Ì Â}.
In this case, an operator ~ is introduced: |t| ® |t|.
The operator ~ constitutes the “meaning” of the logical symbol of negation Ø of the system to be considered [9]. This way, a four-vertex lattice associated with the Annotated Paraconsistent Logic with annotation of two values (PAL2v) may be presented as in Figure 1.
The first element (m) in the ordained pair (m, λ) is the degree in which the favorable evidences support the proposition P, and the second element (λ) represents the degree in which the unfavorable evidences, or contrary, deny or reject the proposition P. Thus, the intuitive idea of the association of a annotation (m, λ) to a P proposition means that the degree of favorable evidence in P is m, and the degree of unfavorable (or contrary) evidence is λ.
In an intuitive manner [9], in such Lattice we have the annotations:
(1, 0) → indicating existence of total favorable evidence and unfavorable zero evidence, attaching a true logical connotation to proposition P.
(0, 1) → indicating existence of zero favorable evidence and total unfavorable evidence, attaching a connotation of falsity logical to proposition P.
(1, 1) → indicating existence of total favorable evidence and total unfavorable evidence, attaching an inconsistency connotation logical to proposition P.
P(m, λ): T = Inconsistent = P(1, 1), F = False = P(0, 1), t = True = P(1, 0), ^ = Indeterminate = P(0, 0)
(0, 0) → indicating existence of zero favorable evidence and unfavorable zero evidence, attaching an indeterminate logical connotation to proposition P.
The formula (ØA) is read “the negation or weak negation of A”; (A Ù B), “the conjunction of A and B”; (A Ú B), “disjunction of A and B”; (A ® B), “the implication of B by A”.
The LPA language, the semantics of a complete set of connectives, axioms is find with details in [3,6,12].
2.2. Algebraic Interpretations of PAL2v in an Unitary Quadrant of the Cartesian Plane
For the better representation of an annotation, and also for practical uses of the τ Lattice in the Uncertainty treatment, some algebraic interpretations involving an unitary quadrant of the Cartesian plane (UQCP) and the representative diagram of the PAL2v will be made.
Initially a system of Cartesian coordinates is adopted for the plane, and the annotations of a given proposition P will be represented by points of the plane [9]. We call unitary quadrant of the Cartesian plane (UQCP) the τ Lattice with the system of coordinates, as proposed in Figure 2(a). Therefore, there is an association of T at (11), ^ at (0, 0), F at (0, 1) and t at (1, 0). In UQCP the values of Favorable Evidence Degree m are exposed in the axis x, and the values of Unfavorable Evidence Degree λ in the axis y.
For each adopted system of coordinates, the annotations (m, λ) of τ are identified by different points in the plane. In the system of Figure 2(a) a given annotation (m, λ) may be identified with the point of the plane in another system, as in Figure 2(b). As a system of coordinates may be fixed on τ, we then define three transformations.
2.2.1. Increasing in the Scale of (as in Figure 3(a))
(as in Figure 3(a))
This increase is given by linear transformation:
 ; whose matrix is:
; whose matrix is:  .
.
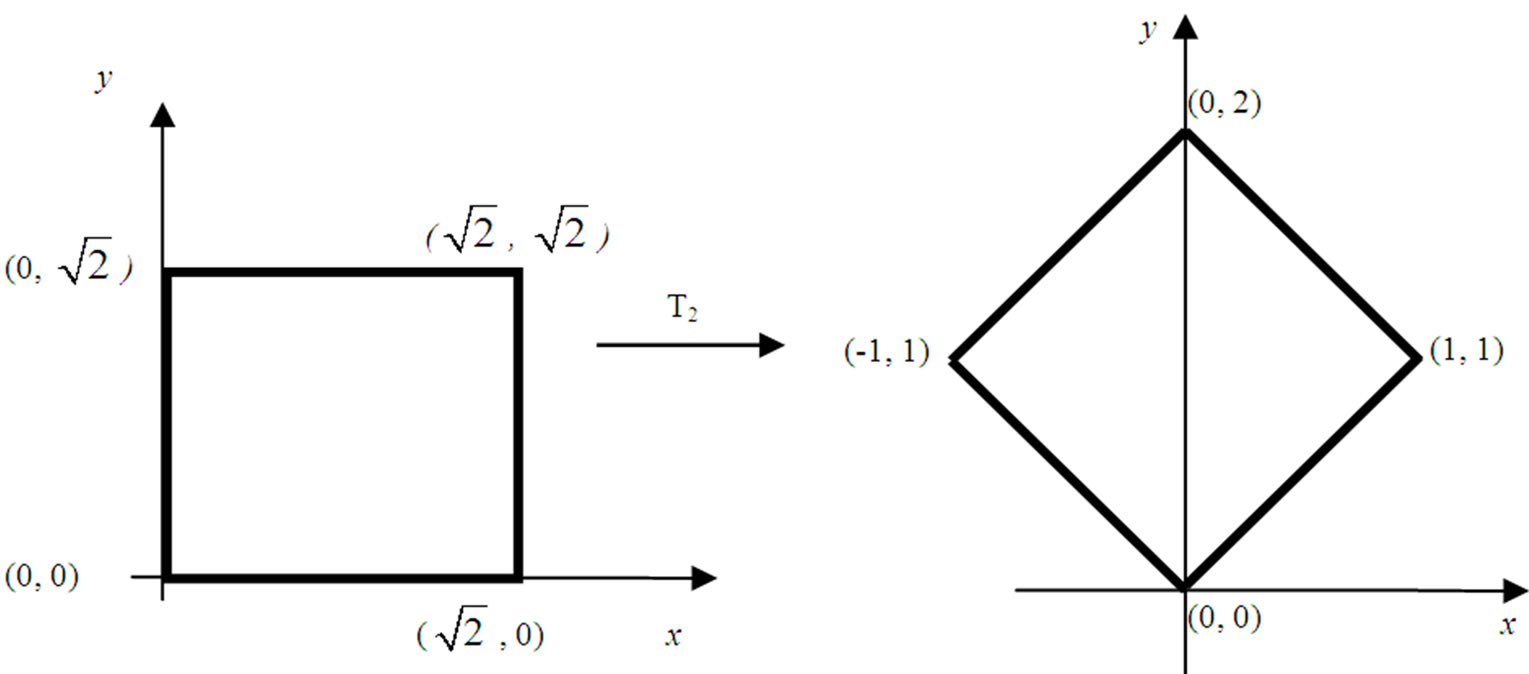
2.2.2. 45˚ Rotation in Relation to the Origin (as in Figure 3(b))
This rotation in relation to the origin is given by the linear transformation:
 (a)
(a)  (b)
(b)
Figure 2. (a) Unitary quadrant in the Cartesian plane (UQCP); (b) τ diagram supplied with a new system of coordinates.
 (a) (b)
(a) (b)
Figure 3. (a) Increasing in the UQCP scale of  ; (b) 45˚ rotation.
; (b) 45˚ rotation.
2.2.3. Translation (as in Figure 4)
This translation is given by: T3(X,Y) = (x, y – 1)
Through the composition T3 ө T2 ө T1 we obtain the final transformation represented by the equation:
 (1)
(1)
Combining the components of the transformation T(X,Y) as the usual PAL2v, we obtain:
 → Favorable Evidence Degree
→ Favorable Evidence Degree
 → Unfavorable Evidence Degree From the first term (X) from the equation of the final transformation, we have:
→ Unfavorable Evidence Degree From the first term (X) from the equation of the final transformation, we have: , which is denominated of Certainty Degree (DC). Therefore, the Certainty Degree of the PAL2v analysis is obtained:
, which is denominated of Certainty Degree (DC). Therefore, the Certainty Degree of the PAL2v analysis is obtained:
 (2)
(2)
Its values, which belong to the set Â, vary in the closed interval +1 and –1, and are in the horizontal axis of the Lattice, called “degrees of certainty axis”.
When DC results in +1 it means that the logical state resulting from the paraconsistent analysis is true t, and when DC results in –1 it means that the logical state resulting from the paraconsistent analysis is false F.
From the second term (Y) of the final transformation, we have:
 , which is denominated Contradiction Degree (Dct). Therefore, the Contradiction Degree of the PAL2v analysis is obtained by:
, which is denominated Contradiction Degree (Dct). Therefore, the Contradiction Degree of the PAL2v analysis is obtained by:
 (3)
(3)
Its values, which belong to the set Â, vary in the closed interval +1 and –1, and are in the vertical axis of the diagram, called “degrees of contradiction axis” [9].
When Dct results in +1 it means that the logical state resulting from the paraconsistent analysis is inconsistent T, and when Dct results in –1 it means that the logical state resulting from the paraconsistent analysis is indeterminate ^.
2.3. The Real Certainty Degree Value
A decision system working with information coming from database of uncertain knowledge will be stronger when at the end of the analyses it shows certainty values which consider the effect of the influence of the inconsistencies coming from conflicting information [1,5,9,12]. The analyses in the lattice of the PAL2v allow us to, after the treatment of uncertain information; obtain a lower Degree of Certainty value due to the effect caused by the contradictions [9]. The value of the Degree of Certainty (DC) to be considered apart from the effect caused by the contradictions is called Real Certainty Degree (DCR). We may calculate the value of the Real Certainty Degree (DCR) from the value of the Degree of Certainty (DC) obtained by the analyses of the lattice of the PAL2v— equation (2). This can be made in the following way: Let us consider that in a paraconsistent analysis the calculations of the Certainty Degrees (DC) and Contradiction Degrees (Dct) resulted in positive values and are interpolated in the diagram in an internal point (DC, Dct), as in Figure 5(a). The point (DC, Dct) is a Paraconsistent logical state ετ, that it is an only point inside of the PAL2v Lattice. In the Figure 5(b) the Cartesian distance d, between the point of the maximum degree of certainty t, represented in the right vertex of the Lattice, and the interpolation point (DC, Dct), or local of the Paraconsistent logical state ετ, is calculated as:
 (4)
(4)
Projecting the distance d in the degrees of certainty axis we can have the point whose value will be considered the Real Certainty Degree value (DCR).
 (5)
(5)
If the calculated Degree of Certainty (DC) result in negative value, as in Figure 5(a), the distance d will be terpolation (–DC, Dct). Therefore, in these conditions, obtained from the point of certainty F, represented in the
 (a) (b)
(a) (b)
Figure 4. Translation of values between UQCP and the PAL2v diagram.
 (a) (b)
(a) (b)
Figure 5. Determination of the Real Certainty Degree (DCR)—Resulting value in the Lattice of the PAL2v.
left vertex of the Lattice, to the point of internal inprojecting the distance d in the degrees of certainty axis we can have the point whose value will be considered the Real Certainty Degree (DCR).
 (6)
(6)
After the determination of the Real Certainty Degree the answer of a paraconsistent analysis should present as value of the Interval of Certainty calculated by:
calculated by:
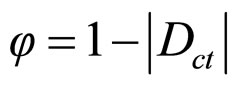 (7)
(7)
Therefore, the output signal of a paraconsistent system of treatment of uncertainties, when receiving the values of evidence in its inputs, will produce an output as such:
 and
and 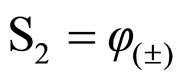
where: DCR = Resulting Real Certainty Degree, such as:
 if: DC > 0 (8)
if: DC > 0 (8)
or 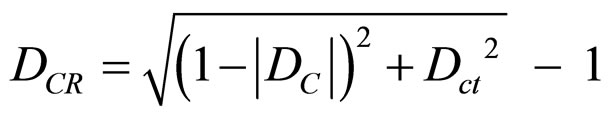 if: DC < 0 (9)
if: DC < 0 (9)
 Signaled Interval of Certainty, obtained by equation (7):
Signaled Interval of Certainty, obtained by equation (7): 
where:  if Dct > 0 or
if Dct > 0 or  if Dct < 0 The Real Evidence Degree of the output can be calculated by the equation:
if Dct < 0 The Real Evidence Degree of the output can be calculated by the equation:
 (10)
(10)
With equations (7) and (10), the system of paraconsistent analyses will present in its output the value of the Real Evidence Degree (μER) with the signaled Interval of Certainty (φ(±)) [9].
3. Paraconsistent System for Treatment of Uncertainties
Using the paraconsistent equations we can compute values that are representative of information signals. Therefore, with the LPA2v algorithms we can construct paraconsistent systems able to present satisfactory answers from information searched in a data base of uncertain knowledge [9].
3.1. Extraction of Evidence Degrees
The paraconsistent system for treatment of uncertainties may be used in many fields of knowledge where incomplete or contradictory information will receive an adequate treatment through the equations of the PAL2v. For this, the signals which will represent the evidence in relation to the proposition in analyses must be normalized and all the processing will be done in real closed interval between 0 and 1 [9]. This process for modelling the evidence degrees with linear variation can be made in its simpler form with the algorithm that will be described in the next section [13-15].
3.2. Algorithm for Modelling/Extraction of Evidence Degrees (Inputs of the PAL2v Algorithm)


Algorithm: Extraction of Evidence Degrees-Mode:variation linear and directly proportional. ;
Figure 6 shows the Discourse Universe (or Interval of Interest) for the extraction of an Evidence Degree using the previous algorithm.
With the change of the equation the extraction of the Evidence Degree can be made with other types of variation. In this manner, the variation type that better represents the analyzed Physical System is chosen for the extraction of the Evidence Degree [9]. This procedure will be shown with details in the example of the section 4 when electric tension is used in the analysis of overload risk.

Figure 6. Graphical representation of the algorithm of extraction of the Evidence Degree with characteristics of directly proportional variation.
3.3. Paraconsistent Signal Information Treatment
The main LPA2v Algorithm used in paraconsistent analyses is the PAN-Paraconsistent Analyzer Node. In an Intelligent system that works with Paraconsistent Logic some PANs are linked forming uncertainty analysis networks (PANnet) for signal information treatments [14-16]. The PAN Algorithm is shown with details in the next section.
3.4. Algorithm for Paraconsistent Analyses (PAN-Paraconsistent Annotated Node)
The PAL2v algorithm of paraconsistent analyses to find the value of the Real Certainty Degree of and the Interval of Certainty is the PAN-Paraconsistent Annotated Node:


Algorithm: PAN-Paraconsistent Annotated Node. ;
4. Example of Application of the PAL2v
The methodology used in this paper to make the mathematical treatment of signals from database of uncertainty knowledge is completely based on the concepts of Paraconsistent Logics. Therefore, the information that was considered uncertain or contradictory can be represented by annotations.
The annotation values are represented in the representative Lattice of the Paraconsistent logics with annotation of two values (PAL2v).
A typical system for uncertainty treatment based in Paraconsistent Annotated Logic with annotation of two values—(PAL2v) may be seen in Figure 7 [14-16].
We consider now a numeric example of the use of the Paraconsistent Logic in analysis and decision-making:
At the beginning we suppose the information source 1 presents a signal to the system valued in 0.87 and the information source 2 presents a signal valued in 0.68.
μ1 = 0.87 and μ2 = 0.68 With representation of the annotation considering the information source 2 as the source of the Unfavorable Evidence, then the complement of μ2 is calculated to obtain the value of Unfavorable Evidence Degree:

The annotation (μ, λ) is represented as: .
.
Therefore, the Paraconsistent Signal that results from this condition is represented as: 
From equation (2), the Certainty Degree (DC) is:
 . Therefore:
. Therefore: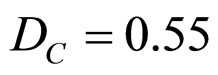 .
.
From equation (3), the Contradiction Degree (Dct) is:
Therefore: .
.
From equation (4), the distance d is:

Since the Certainty Degree (DC ) is positive we determine the Real Certainty Degree from equation (8):


From equation (7) the Interval of Certainty is:

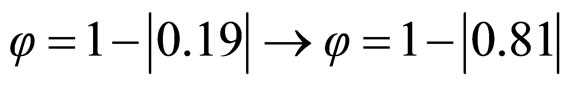
as Dct is positive, then the Signaled Interval of Certainty is: 
The Interval of Certainty is the indicative Paraconsistent Logical signal for help the decision-making.
From the value of the Real Certainty Degree we calculate the value of the Real Evidence Degree through equation (10): 
Being: 
then
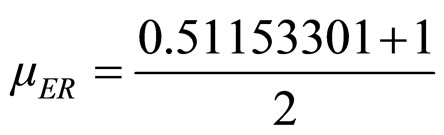

In Paraconsistent analysis Systems the Intensity of the Real Evidence Degree (μER) is used as main value to decision making.
The Paraconsistent Analysis Network—PANnet
A network for treatment of uncertainties can be built with several interlinked PAN-Algorithms. With this process of normalization will exist at each PAN output a Resultant Real Evidence Degree value accompanied by a Resultant Interval of Certainty value.

Figure 7. Typical system for Paraconsistent Analysis of two inputs.
The Interval of Certainty value will indicate how the level of contradiction in the analysis is in real time. Thus, besides the information about the certainty in relation to the proposition, the Paraconsistent Analysis Network will also have conditions to estimate the capacity of analysis and control the results by means of feedback.
In this work the PAN algorithms are not used like analyzer Nodes in Neural Artificial Network as seen in [17,18], however they can be adapted for that function. That procedure is possible because the same concepts of PAL2v are used in interlinked learning cells in Paraconsistent Neural Artificial Networks as it was presented in [9,16].
The real applications of PANnet in Analysis Systems of Artificial Intelligence are described in [13-16] and an example of this application is shown to follow:
Now we show an example of application of the paraconsistent analyses to evaluate risks of overloads in an electric circuit [14,15].
The proposition is:
P = The electric System is in Overload Risk state.
In this example, initially the Algorithm for Modelling/Extraction of Evidence Degrees for the inputs of the PAL2v Algorithm is applied to get the two first evidence degrees. From measured values; Temperature T, Electric Tension V and Electric Current A are obtained the normalized values in the form of Evidence Degrees according to the linear variation in specified universe discourse.
Temperature T → Information Source 1 The Universe of Discourse is:
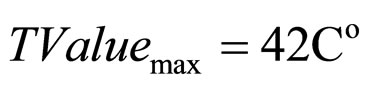 and
and 
The measured value is: .
.
For an Electrical system, the high Temperature value means high risk of overload.
As: , then:
, then:


Electric Tension V → Information Source 2 The Universe of Discourse is:  and
and 
The measured value is:

For an Electrical system, the low value of the electric Tension means high risk of overload, therefore the equation of the tension must be for a linear and inversely proportional characteristic. In this manner the equation is:

For: 
For 

For 

As: 
then: 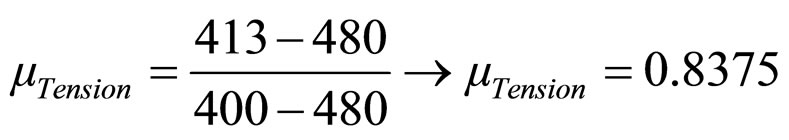
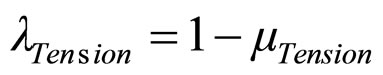


The Paraconsistent Logical signal is:

After this initial analysis the PAN Algorithm is applied with the Evidence Degree of the Temperature (Favorable) and Evidence Degree (Unfavorable) of the Electric Tension (TàV):
Certainty Degree (DC) is:


Contradiction Degree (Dct) is:



As  then:
then: 
Resulting in a Real Evidence Degree:


The Interval of Certainty from equation (7) is:

As: (µ + λ) < 1 then Signaled Interval of Certainty is:

The Real Evidence Degree and Interval of Certainty are in the fifth column of the Table 1.
The extraction of the Evidence Degree of the Electric Current is made using the algorithm:
Electric Current A → Information Source 3 The Universe of Discourse is:
 and
and 
The measured value is: 
For an electrical system, the high value of the electric Current means high risk of overload.
As:  then:
then:




Table 1. Results of an application example in Electric Power System.
Universe of Discourse: Temperature: 25˚C → 42˚C; Electric Tension: 480 V → 400 V; Electric Current: 23 A → 34 A. Linear Variation: ◊ Logical Paraconsistent Analysis.

After that second analysis the PAN Algorithm is applied with the Real Evidence Degree of the fifth column (Favorable) and the Evidence Degree of the Electric Current (Unfavorable) ((TàV)àA):
The new Paraconsistent Logical Signal is:

Certainty Degree (DC) is:


Contradiction Degree (Dct) is:



As 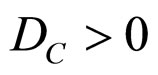 then:
then: 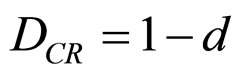

Resulting in a Real Evidence Degree:



The Interval of Certainty:

As: (µ + λ) > 1 then 
After the Paraconsistent Analysis between Temperature, Tension Electric and Current Electric the Resulting Evidence Degree (μER) considered as the Overload Risk Degree of the measured point.

This method of treatment of Uncertainties is being used in Electric Power System of the AES-Eletropaulo Company and EDP Bandeirantes in Brazil [13-15].
5. Conclusions
The algorithms presented in this paper are based in paraconsistent logics, therefore they were conceived to receive uncertain and contradictory information, equate their values and present results, with no restrictions regarding conflicts that may be present in the information signals. Through the analyses in the lattice, we obtained simple equations, which made easier the construction of PAL2v algorithms for the development of Expert Systems able to work with the treatment of uncertainties.
The obtained PAL2v algorithms may be easily reproduced by means of any computer language or hardware tool, therefore they are possible of application in several fields of Artificial Intelligence. In the paraconsistent model for the treatment of uncertainties we may cross many nodes—PANs or information system analyses, as the one presented. These PAN configurations will constitute paraconsistent networks of decision (PANnet), which, unlike the known systems, the weight of the information conflicts will not bar the answers, but, through a new approach, new conflicting data treatments will be taken, producing information which are relevant for decision making.
This new method for treatment of uncertainties differs from the ones previously known, because with this technique we can give a convenient treatment to the contradictory signals. The application of the PAL2v presented in this work opens good perspectives for the increase of research that involves decision making systems.
6. Acknowledgements
The author thanks Gilberto A. T. de A. Holms for his assistance during this research.