Urban Growth and Its Impact on Cityscape: A Geospatial Analysis of Rohtak City, India ()
1. Introduction
Rohtak town is one of the eight Priority Towns (Regional Centers) of National Capital Region Regional Plan 2001 prepared by the National Capital Region Planning Board in consultation with the State Governments. The Board was formed in 1985 in order to provide balanced development of the region. It extends its influence on the areas falling on its outskirts in the states of Uttar Pradesh, Rajasthan and Haryana.
The Plan had projected for Rohtak a population of 500,000 by 2001 AD against census population of 1.67 hundred thousand in 1981 and 2.16 hundred thousand in 1991. Its gross density was proposed 110 persons per hectare up to 500,000 persons.
The strategy for development of the settlement system, as per NCR Regional plan 2021, allows other towns of the NCR to develop within their carrying capacity and development potential, as may be determined by the Development/Planning Agencies of the constituent States of the NCR. The Plan has envisaged that these regional centres will perform highly specialized secondary and tertiary sector activities for providing job opportunities, which cannot be provided by the lower order centres. These centres, according to the NCR Plan, will be developed for advanced industrial and other economic activities and will have concentration of administrative and higher order service functions, which are expected to exert an increasingly dynamic influence on attraction of investment.
Keeping in view its policies as well as increasing demand of land due to employment potentials and commercial base, the Government of Haryana notified the Revised Final Development Plan vide Town and Country planning department, Notification No. CCP (NCR) R-C. A./98/1464 dated the 3rd September, 1998 and published in the Haryana Govt. Gazette. (Extra) on 8th September, 1998 for a population of 700,000 by 2031 AD including the Controlled Areas, with gross density of 110 persons per hectare [1]. This low density has been kept for providing more sectors for development towards Delhi side keeping in view the contemporary trend of growth.
Although the location of the town does suggest that it has great potentials for industrial development through induced growth, the town has only limited industrial units resulting into a weak economic base for the town. As such the development of the town has not taken place to the desired extent, keeping pace with the envisaged population of 500,000 by 2001 as per the Regional Plan. The new economic environment poses new challenges to urban governance in the country. The urban local bodies have to be financially viable. In order to meet their budgetary expenditures they have to mobilize resources and tax collection efficiently. Moreover, Rohtak municipality has been accorded the status of Municipal Corporation. Large newly added land is to be put to various uses. Hence the question of sustainable development and management of land.
2. Study Area
Rohtak city is located at the intersection of 28˚41'1'' North latitude and 76˚12'42'' East longitude in the NCR region of Haryana on National Highway No. 10. Spread over 100.57 km2, it lies 70 kms north-west from Delhi and 240 kms south of Chandigarh (Figure 1), the state capital.
2.1. Journey from a Town to a Municipal Corporation
The initial site of the city was a mound. According to K. D. Sharma [2] the reasons for the emergence of the settlement nucleus were: 1) its location on the southern edge of the Kuru jangala, a thick forested area; 2) its location on an important trade route called Uttarapatha; and 3) its vicinity to Hastinapur, the capital of Kuru Mahajanapada in the Ancient period. In the Medieval period the vicinity of the city to Delhi and its location on the politically and strategically important Delhi-Multan road helped it to flourish as a trade centre and a strategic place. During the British period the site of the city expanded like that of any other British district headquarters town. During the post-partition period of the country a large number of displaced persons were rehabilitated. In fact, displaced persons formed 50% of the total population of Rohtak in 1951. The economic reforms ushered in the country in 1991 did not have any substantial impact on the growth of the city. It was taken over by other towns namely, Faridabad and Gurgaon in the periphery of Delhi consequent upon the policies of the govt. And their locational advantage in the changed economic environment. Rohtak, an ancient settlement, became a Class-I city with a population of 1.25 lakhs in 1971 which more than doubled to 2.95 lakhs in 2001 [3]. There was a commensurate increase in areal extent from 11.66 km2 in 1971 to 29.58 km2 in 2001 [4]. The city space had become less dense. With inclusion of sector I of HUDA (1.20 km2), it acquired the status of urban agglomeration in 2001 (Table 1).

Figure 1. Geographic location of study area.

Table 1. Rohtak city: area, population and density, 1961- 2011.
Rohtak city was accorded the status of Municipal Corporation on 17 March, 2010 vide notification of the Government of Haryana [5].
The city has experienced a transition from Municipal Committee to Municipal Council and presently Municipal Corporation. Haryana Municipal (Amendment) Act, 1994 identifies “Municipality” as an institution of self-government constituted under section 2A which may be Municipal Committee or a Municipal Council or a Municipal Corporation.
1) “Municipal Committee” is a transitional area with population not exceeding fifty thousand;
2) “Municipal Council” is a smaller urban area with population exceeding fifty thousand but not exceeding three lakhs and 3) “Municipal Corporation” is a larger urban area with population exceeding three lakhs, to be governed by a separate Act: Provided that a municipality under this section may not be constituted in such urban areas or part thereof as the State Government may, having regard to the size of the area and the municipal services being provided or proposed to be provided by an industrial establishment in that area and such other factors as it may deem fit, by notification, specify to be an industrial township [6].
Provided further that no military cantonment or part of a military cantonment shall form part of a municipality.
Further, “a transitional area”, “a smaller urban area” or “a larger urban area” means such area as the State Government may, having regard to the population of the area, the density of the population therein, the revenue generated for local administration, the percentage of employment in non-agricultural activities, the economic importance or such other factors as the State Government may deem fit, specify by notification for the purpose of this section.
Resultantly the cityscape has experienced jurisdictional change with incorporation of eight revenue villages. The areal extension is more along the national highway leading to Delhi. It presently occupies 100.57 km which is more than threefold increase when compared to 2001 and includes 8 villages namely; Sunari Kalan, Sunari Khurd, Kanehli, Majra, Kheri Sadh, Bohar, Asthal Bohar and Garhi Bohar (Figure 2).

Figure 2. Areal extension of Rohtak city, 1971-2010.
The density of population has declined substantially. Much of the newly added land is agricultural. The urban growth and subsequent land use change in the city is likely to affect sustainable use of land.
Physiographically, the heart of the town is of bowl shape. Besides this, there are other pockets where discharge of storm water though gravity is not possible and as such pumping system is the only remedial measure. Also, the human interference with the natural lines of drainage of the site, especially the construction of the Gohana and Delhi railway lines, has also resulted in the flooding of the city during periods of heavy rainfall. The ground water being brackish, water supply is canal based. Although there are two water works, one along Sonipat road and other along Jhajjar Road but their remains acute shortage of water supply in the town.
3. Objectives
The study attempts to examine the urban growth and trend of development of Rohtak city and its impact on land use change between 1983 and 2010.
4. Material and Method
Present study is based on the remote sensing spatial as well as the non-spatial data available from the various sources for different periods. The sources are Census of India [7], Statistical Abstract of Haryana, Town and Country Planning, District Gazetteer of Rohtak district and Town directory of Haryana. Land use map of the study area for 1983 was acquired from the Survey of India Guide Map whereas Cartosat-1 and LISS-IV image with 2.5 meter and 5.8 meter resolution of 2010 was accessed from National Remote Sensing Centre, Hyderabad and digitized into the GIS environment using on-screen digitization. Topographic Sheet No. H43W9 at scale of 1:50,000 is used for the geo-referencing of Guide Map and Cartosat- 1and LISS-IV image. The study is based on supervised classification and visual interpretation of the Guide map and satellite imagery. (See Figure 3) Field survey was performed throughout the study area using Global Positioning System (GPS) and obtained accurate location point data for each land use class included in the classification scheme. The 1983 land use map depicts a situation that existed 27 years before the Cartosat-1and LISS-IV image of 2010. Hence, the 1983 map could not be checked against the ground truth but, the available historical data for the study area were used to validate the interprettation made. However, Cartosat-1 and LISS-IV images digitised data of 2010 was directly checked against ground truth throughout the study area. Canal and major roads are digitised in linear as well as polygon features. The change in respect of public utilities and facilities could not be seen for lack of information in 1983 guide map. Remote Sensing and GIS techniques have been used to find out the land use changes in the Rohtak city from 1983 to 2010. ERDAS 9.0 software has been used for the geo-referencing of spatial data. Arc GIS 9.3 software has been used for the digitization, integration, overlay and presentation of the spatial and non-spatial data of land use change in the city. A third level classification (Table 2) has been used for the urban land use analysis of Rohtak city which is based on National Urban Information System (NUIS) manual, 2008 [8]. Urban development has led to manifold expansion of the cityscape of Rohtak leading to changes in land use. The study specifically focuses on interpreting city’s land use change pattern and growth based on satellite and demographic data. The study area of Rohtak city is the Municipal Corporation boundary. Guide Map, Cartosat-1, LISS-IV images and Census data are used to identify different patterns of land use/land cover changes and growth of the city. A database is built to identifying between landscape changes and urban growth. The technique is possible to verify the pressure exercised by the urban growth on the agricultural areas and is to identify the recent spatial configurations. This comparative approach has demonstrated how landscape changes can be derived from satellite imagery and guide map in the urban spatial structure. Interpretation of Rohtak’s growth over a period of 27 years allows a deeper understanding of growth mechanisms, underlying drivers of urban expansion, and their effects on local livelihoods.
5. Population Growth
One of the important towns historically, Rohtak city’s population growth was much lower than the state of Haryana. However, the decade 2001-2011 has been significant
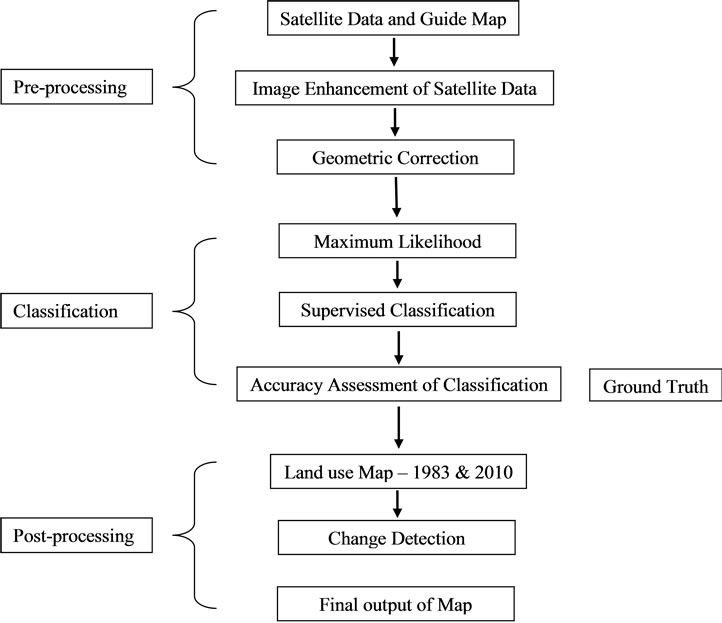
Figure 3. Methodological flow chart of land use classification.

Table 2. Urban land use classification.
when the process of extension in territorial jurisdiction in its urban area was most pronounced. It saw an addition of nearly 71 km2 of area and an adding up of more than 1.5 lakh population.
6. Land Use Analysis
Analyzing the spatial and temporal changes in land use and land cover (LULC) is one of the effective ways to understand the current environmental status of an area and ongoing changes. Urbanization is a major cause of land use changes and land conversions. It makes unpredictable and long lasting changes on the landscape. An important aspect of is to determine what is actually changing to what i.e. which land use class is changing to the other. The information on land use change reveals both the desirable and undesirable changes and classes that are “relatively” stable overtime. This information serves as a vital tool in management decisions and policy formulation [9]. The land use maps of two points of time, that is, 1983 (Figure 4) and 2010 (Figure 5) extracted from Guide Map and satellite image based on visual interprettation respectively depict land use categories such as residential, agriculture, public and semi-public, commercial, industrial, transport and communication, vacant land, plotted land, water body, recreational area, forest, rural settlement and wasteland.
6.1. Rohtak City: Land Use in 1983
The city had added nearly 11.00 km2 area to its existing boundary in 1981 census. Consequently, agriculture emerged as the dominant land use class in 1983. It occupied an area of 9.04 km2 i.e. 33.17% of the city area followed by public semi-public and residential area i.e. 20.70% and 20.59% respectively. Public and semi-public area includes place of work, education, religious activities, health, medical and social-cultural centre. The city besides being a district headquarter is also functioning and accommodates a large number of public and semi-public offices, schools, colleges, university and the only medical college in Haryana, Tilyar Tourist Complex, to name a few. Urban core, which represents the traditional part of the city, is high-density area used for the residential, commercial, public and semi-public purpose. Being an old, traditional town the different land uses are interspersed with each other and not mutually exclusive.
6.2. Rohtak City: Land Use in 2010
In 2010 also the agricultural land has increased because of the extension of municipal boundary and substantially giving way to urban development of Rohtak city. It presently covers an area of 100.57 km2 which is under different uses shown in the map. Presently, more than 2/5th land is under agriculture (44.21%). Residential use covers 20.44% of the total area and public and semi-public 8.24%. 2.88% and 2.06% area is devoted to rural settlements and transport and communication respectively. 8.82 km2 land is kept for the development of sectors for residential and other purposes. Notably, there is absence of forest cover in 2010. Also, the area under wasteland has increased.
6.3. Analysis of Change Patterns: 1983-2010
The change is observed for a period of 27 years between 1983 to 2010 in percentage and area shown in km2 within each land use class (Table 3). All types of land use enumerated above have undergone expansion in varying degrees except vacant land, forest cover and wasteland. The area under vacant land has slightly declined, there is no forest cover and wasteland has increased appreciably. Urbanization has usurped rich agricultural land. The size of the latter has increased from about 9 km2 in 1983 to nearly 45 km2 in 2010. The rich agricultural land would be put to other uses in times to come and this could be true of many other towns.
Real estate is likely to see more activity in future. It is not only seen as a safe long term investment among all sections of the society who have additional surplus income to save but also as a highly lucrative for the middlemen and the promoters of real estate ventures who orchestrate and boost up the market value of land. The change in urban built-up residential area is also substantial indicating urban growth. There is four-fold increase in residential area from 5 km2 to 20 km2. Most of the change in residential category is the conversion of vacant land and agricultural land to residential in the low density areas and along major roads. There is increase in agriculture land due to extension of city boundary. The spatial growth or expansion in other land cover types has directly taken place on the agricultural and vacant land. The breakdown of joint families to the growing culture of nuclear family and high population density increased the demand for housing resulting in the process of land conversion becoming more precipitous. Most low density planned settlement is HUDA sectors of the city which are the product of urban sprawl. Besides, eight rural settlements form part of the municipal corporation of Rohtak.
The urban sprawl is along the state and national highways. In fact there has been substantial road development, construction of over bridges on the entry and exit points of the city, widening of the roads within the city by removing encroachments. The outward expansion of the ring-road system is found to be one of the most important driving forces explaining the temporal and spatial pattern of land use change.
Area under Plotted land that includes land ear-marked for sectors, model Industrial Township etc. has increased. Some part of this land is earmarked for development of HUDA sectors and also given to privatebuilders to develop residential colonies. Most of this land is along the National Highway 10 leading to Delhi and National Highway 71. Industrial area has also increased somewhat. A new Industrial Model Township has been built to attract investment that would inject some economicdynamism to the city.
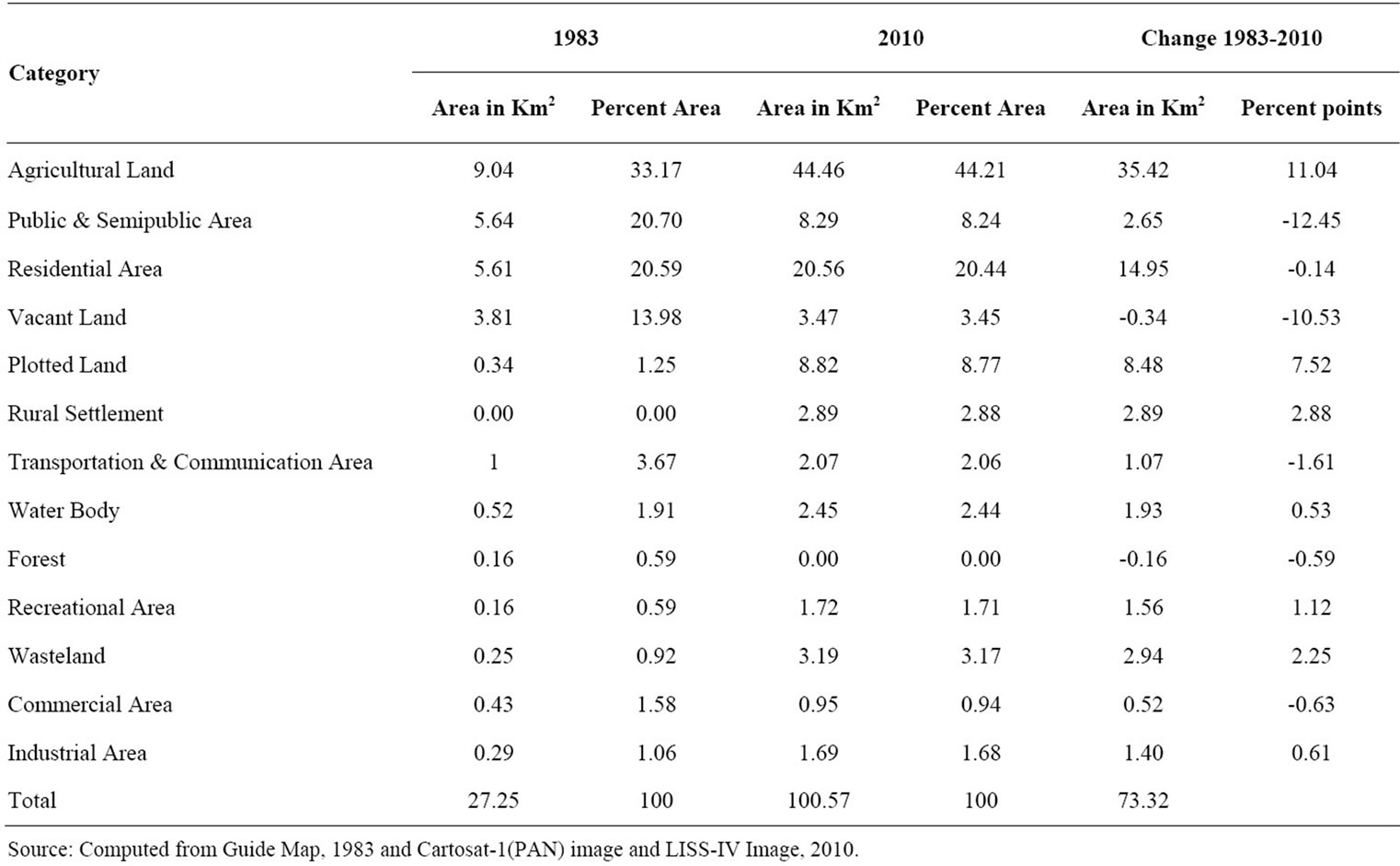
Table 3. Land use and Change Pattern in Rohtak City: 1983-2010.
7. Concluding Remarks
An attempt has been made to discern spatial patterns of land use for Rohtak city over a period spanning more than two and half decades beginning 1983. The requisite information has been systematically mapped, monitored and accurately assessed from satellite data accompanied with conventional ground data. Rohtak city has gained both in terms of population size and area. A substantial increase in the urban population is due to net rural-urban classification. Increase in areal extent has come with inclusion of eight rural settlements within the municipal corporation boundary that have to be integrated with the city.
Addition of large number of people has implications for provision of infrastructure and civic amenities. Apart from being plagued by gaps in infrastructure to service the current population, the city faces other common challenges like erratic power supply, strain on civic supplies like water and drainage in some of parts, accumulation of garbage, pollution. Geographically, there is a clear shifting of urban land construction from the inner city to the outskirts as a consequence of urban sprawl.
The city lacks vegetation cover. Needless to say that vegetated and open green spaces (parks) are the most important parameters of quality of urban environment assessment. Hence, a vigorous focus needs to be given to grow more trees and also develop green belts that can reduce a city’s ecological footprint and carbon emissions significantly. A suitable strategy to reclaim wastelands is required.
The extent and pace of urban transformation will raise concern about the city sustainability. As the city grows in size and population, harmony among the spatial, social and environmental aspects of a city and between its inhabitants becomes of paramount importance. There is a need for equitable distribution of public resources and balanced spatial and territorial development, particularly through investments in urban infrastructure and services. What innovative approaches can we adopt to urban planning and management that are inclusive, pro-poor and responsive to threats posed by environmental degradation and global warming? Enlightened and committed political leadership combined with effective urban planning, governance and management that promote equity and sustainability are the critical components to the building of healthy and harmonious city.