Modeling of the Electrical Conductivity of Graphite Dispersions in Electrolytes ()
1. Introduction
Studies of the electrical conductivity of coals dispersions are important because they afford a basis for receiving information about the structure of the electric double layer (EDL) and are used in technological processes, such as flotation, hydrotransport of coals suspensions, regulation of aggregative stability of dispersions. In connection with the urgency of research in this direction, the electric conductivity of graphite suspensions in potassium chloride solutions in the alternating and constant electric fields has been measured.
The nature of the electrical conductivity of disperse systems is determined by the dispersed phase properties and the dispersion medium, the processes of aggregation of the particles which conduct electric current. Thus, in accordance with the work [1], the electrical conductivity of graphite suspension depends on the particle aggregation, and the present paper proposes a model which explains the dependence of the electrical conductivity on the concentration of the dispersed phase [2]. It should be noted that the authors of the papers [1,2] explained the increase in the electrical conductivity of graphite suspensions in dilute electrolytes only by the particle aggregation and did not take into account the electrical properties of the particles; therefore, the interpretation of the results stated in the mentioned works is debatable.
The rheological properties of the graphite dispersions have been studied and it has been concluded that the graphite particle aggregation occurs at relatively high concentrations of the dispersed phase and they exceed 15% (mass.) [3,4]. At the graphite concentrations corresponding to the so-called “threshold of the electric current flow”, there is an increase in the plastic viscosity and in the limit shift stress of the heterogeneous system.
Studying the particle aggregation by measuring the electric conductivity, the following should be noted. The particle aggregations of the dispersed phase influences the electrical conductivity of the heterogeneous system only in case the particles form chain structures and are aggregated along the current lines [5]. In a heterogeneous system without any chain structures of equal concentrations of the dispersed phase, the electrical conductivity is a topological invariant relative to the system dispersion [6]. The equation showing the dependence of the electrical conductivity on the dispersed phase concentration is as follows:
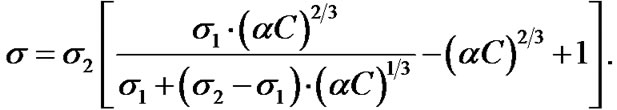 (1)
(1)
Here α, C are respectively the ratio of the heterogeneous system densities to the dispersed phase, the mass fraction of the dispersed phase; σ, σ1, σ2 are respectively the electrical conductivity of the heterogeneous systems, the dispersion medium, the dispersed phase, Om–1, m–1.
Provided that ,
,  , the Equation (1) changes respectively:
, the Equation (1) changes respectively:
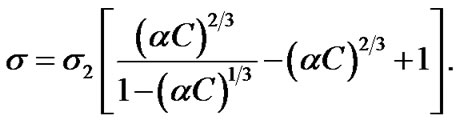 (2)
(2)
 (3)
(3)
2. The Research Objects
As the research objects, graphite S-3 with the basic substance content of 99.9% was used. The graphite was crushed and the fractions with the dispersion of more than 50 microns were sifted out. The submicron fractions with the particle size of less than 0.5 microns were decanted. The particle size distribution was determined on the particle laser analyzer Microsizer 201 C. The main fractions of the particle distribution according to their sizes lay within the range of 5 - 30 mc, Figure 1. The content of the main 7 mc fraction made up 12%.
The electric conductivity was measured with the help of the alternating-current bridge by the compensation method at the frequency of 1000 Hz. The maximum voltage peak value equals to 2 V. The aqueous potassium chloride solutions with the concentrations of 0.0005; of 0.001 and 0.01; 0.1 M have been used as the electrolyte. The measuring cell is a 10 sm3-volume glass container with a thermostat and 1 sm2 platinum electrodes. The suspension was stirred at a speed of 120 rpm. In the constant electric field the electrodes were connected to a voltage source of 40 - 50 V, the volt-ampere dependence

Figure 1. The fractional composition of the graphite dispersions in the coordinates of the percentage composition (P%) —Radius of the particles, micron.
was measured, the electrical conductivity was determined. The experimental measurements have shown that within the 3% - 7% relative measurement error in the constant electric field the electrode polarization can be neglected at a voltage of more than 30 V.
3. Measurement of the Electrical Conductivity of Graphite Suspensions in the Alternating and Constant Electric Field
The increase in the suspension electrical conductivity in the alternating electric field from the dispersed phase concentration (up to the dispersed phase concentrations of 20% mass.) in potassium chloride solutions with the electrolyte concentration of 0.0005 - 0.01 M, Figure 2, was observed.
In 0.1 M KCl the dependence of the suspension electrical conductivity on the mass fraction of the dispersed phase had qualitative differences from dilute solutions. With the increase in the dispersed phase concentration the electrical conductivity did not increase, but decreased, Figure 3. Particles of the coals examined displayed dielectric properties by increasing the ratio of the structural electrical resistance of the suspension. A significant increase in the suspension electrical conductivity was observed at a relatively high suspension concentration with the mass fraction of the dispersed phase of over 15%. This effect is not observed in the work [1] as the upper concentration limit of the electrolyte made up 0.01 M, and the volume fraction of the graphite did not exceed 0.15.
Analyzing the properties of the dispersions, a reasonable assumption can be made: in dilute electrolytes an increase in the electrical conductivity of the system occurs as a result of the electric charge transfer in the electric double layer (EDL) along the current lines of the particle surface layer in accordance with the frequency characteristics of the electric field. In the dilute electrolytes in the alternating electric field the electrical conductivity of the heterogeneous system is composed of the particle and electrolyte conductivity. The equivalent electrical diagram of a graphite particle contains a consecutively connected EDL capacity and resistance. The availability of a developed EDL is a necessary condition for the charge flow when applying the alternating electric field [7,8]. The regularities of electric conductivity changes in the electrolyte indicate the presence of the EDL diffusion component in dilute solutions (0.01; 0.001; 0.0005 M) which prevents the aggregation of the particles and the formation of the current lines that contribute to the electrical conductivity increase.
In 0.1 M potassium chloride solution the electric double layer is not well developed, the surface conductivity

Figure 2. The dependence of the electrical conductivity of the graphite dispersions (from left to right—experimental and calculated values) in solutions of potassium chloride on a mass fraction of the disperse phase in the alternating electric field. 1, 2, 3: respectively experiment 0.01; 0.0005; 0.001; M KCl solution. 1, 2, 3: respectively, the estimated value of 0.01; 0.001; 0.0005; M KCl (T = 298 K).

Figure 3. The dependence of the electrical conductivity of the graphite dispersions in 0.1 M solution of potassium chloride on a mass fraction of the disperse phase. 1, 2: respectively constant and alternating electric field; 3: the calculated values.
and the capacity components have low values, therefore the graphite particles are dielectric-like, Figure 3. The electrical conductivity was calculated according to the Equation (3). In accordance with the calculation there is a decrease in the electrical conductivity, which conforms to the experiment.
Provided that , the electrical conductivity has been calculated according to the Equation (2) for the alternating electric field, the electrolyte concentrations are 0.0005; 0.001; 0.01 M, Figure 2. We should note that the model does not allow accurate prediction of the slope of the curves at the potassium chloride concentration equaling to 0.0005 M. Probably in dilute electrolytes the electrical surface properties should be taken into account (the condition
, the electrical conductivity has been calculated according to the Equation (2) for the alternating electric field, the electrolyte concentrations are 0.0005; 0.001; 0.01 M, Figure 2. We should note that the model does not allow accurate prediction of the slope of the curves at the potassium chloride concentration equaling to 0.0005 M. Probably in dilute electrolytes the electrical surface properties should be taken into account (the condition  is not observed). Within the range of 0.001 - 0.01 M concentrations the model of the electric conductivity of graphite dispersions in the alternating electric field, in accordance with which
is not observed). Within the range of 0.001 - 0.01 M concentrations the model of the electric conductivity of graphite dispersions in the alternating electric field, in accordance with which , should be regarded as satisfactory.
, should be regarded as satisfactory.
In the constant electric field the conductive particle is polarized, the electric field within the particle is compensated in consequence of the charge distribution on the surface. At the ideal polarizability of the surface the conductive particles are similar to the dielectric placed in the electrolyte. Therefore, in the constant electric field the electrical conductivity with an increase of the dispersed phase mass fraction must go down; it occurs in 0.1 M solutions, Figure 3.
In solutions with the KCl concentrations of 0.001 - 0.01 M with the dispersed phase content of less than 15% the decrease in the heterogeneous system electrical conductivity is slight, Figure 4. Probably, it is caused by

Figure 4. 1, 2: respectively, the dependence of the electrical conductivity of the variances of the particles in the constant electrical field in the 0.01; 0.001 M solution of potassium chloride on a mass fraction of the disperse phase.
the fact that coal particles are not ideally polarized—the general regularities of the ideal conductive particle polarizability are presented in [9]. Electrochemical reactions are possible on the graphite surface. Thus, a reversible flow on the surface of additional electrochemical processes to the cathode and anode directions is necessary for the polarized graphite particle discharge and charge. The presence on the surface of a large number of surface compounds containing oxygen and having low discharge potentials—ionization is less than 0.001 V [10] —enlarges the suspension conductivity; therefore, the conformity of the electrical conductivity change to the dispersed phase content is expressed insignificantly.
4. Conclusion
The dependence of the electrical conductivity of graphite dispersions in potassium chloride solutions in the alternating and constant electric fields has been found. The assumption is stated that it is necessary to consider the impact of the EDL on the electrical conductivity of heterogeneous systems in dilute electrolytes (0.0005 - 0.01 M). In 0.1 M potassium chloride solutions the electrical conductivity of the suspensions decreased and then increased, which indicates the aggregation of the particles at the dispersed phase concentration of more than 0.15 (mass.). Different models of the electrical conductivity of graphite suspensions are compared; the electrical conductivity in them is a topological invariant relative to the dispersion of the system.